The Ring Nebula
The diversity of colors, shapes, and sizes of planetary nebulae make them fascinating objects. In this photo release Calar Alto presents a rather unique view combining both optical and near-infrared data of Messier 57, the Ring Nebula.
Text: David Galadí-Enríquez
Image acquired with the 3.5 meter and 1.23 meter Zeiss telescopes at Calar Alto Observatory.

Click to download a full-resolution image.
Image Caption and Credits: Image of the Ring Nebula in Lyra, from the Documentary Photo Gallery of Calar Alto Observatory (Descubre/CAHA/OAUV/DSA). Vicent Peris (OAUV/DSA/PTeam), José Luis Lamadrid (DSA/CEFCA), Jack Harvey (DSA/SSRO), Steve Mazlin (DSA/SSRO), Ana Guijarro (CAHA). Entirely processed with PixInsight 1.5. Click on the image to download a full-resolution version (image scale: 0.15 arcsec per pixel).
More technical information on the acquisition and processing of this image is available in the Processing Examples section of this website, where you'll find a specific processing notes document.
Links to the Images and Related Material
Planetary nebulae
Planetary nebulae are sometimes called cosmic butterflies. In fact, their beauty and variety deserve the comparison. This image of the Ring Nebula is part of the Documentary Photo Gallery of Calar Alto Observatory and follows the previously released image of the Owl Nebula. Although there are many images of the Ring Nebula, the combination of wavelengths of the image released here, and the careful data process, make us look at this popular object with new eyes.
The Owl and the Ring nebulae are different in several aspects but it is easy to appreciate common traits that identify them as obvious members of the category of planetary nebulae.
Planetary nebulae represent the final stage in the evolution of stars whose masses are smaller than eight times that of the Sun. The approach of the final energy crisis that marks stellar old age transforms the star into a red giant whose stellar winds fill their surroundings with a thin envelope composed mainly from hydrogen gas.
Some thousands of years later, the dying star experiences a faster and more violent process that makes it expel all its external layers. Material from these layers builds up the central and more conspicuous part of the planetary nebula, and is composed not only from hydrogen and helium, but also from other heavier elements produced in the stellar interior during its life of billions of years. The nude stellar core remains abandoned in the center of the structure in the form of a white dwarf star. The high temperature of the white dwarf makes it emit ultraviolet radiation, which excites the nebular atoms and makes them glow in a process very similar to what occurs inside neon lamps. This mechanism is responsible for the glow of the denser, inner parts of the nebula, but also of the periphery, the nebular halo, corresponding to material expelled by the star long ago as stellar wind.
The different colors of the inner and outer zones are due to the change in physical conditions depending on the distance to the central white dwarf, but they are related, too, to the contrast in chemical composition between the central region and the halo.
The Ring Nebula in Lyra
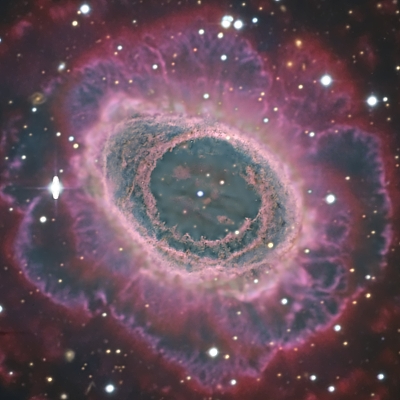 The Ring Nebula is in the northern constellation of Lyra. It was discovered in 1779 by Antoine Darquier de Pellepoix and by Charles Messier. It is included in the catalog of diffuse objects of this second astronomer, with number 57. This nebula is placed at 2300 light-years from Earth. It seems to have begun to form 2000 years ago and it is expanding at a velocity of 20-30 km per second. The surface temperature of the central white dwarf is about 120,000 degrees Celsius.
The Ring Nebula is in the northern constellation of Lyra. It was discovered in 1779 by Antoine Darquier de Pellepoix and by Charles Messier. It is included in the catalog of diffuse objects of this second astronomer, with number 57. This nebula is placed at 2300 light-years from Earth. It seems to have begun to form 2000 years ago and it is expanding at a velocity of 20-30 km per second. The surface temperature of the central white dwarf is about 120,000 degrees Celsius.
Recent studies indicate that this nebula belongs to the bipolar kind, with a central structure shaped like a cylinder or, perhaps, a hourglass. The symmetry axis of this structure is pointing almost exactly towards the Earth, what induces the characteristic ring-like appearance. The external halo is more spherical, although it contains a number of complex structures, as can be seen in the image.
The Image
This photograph combines data obtained through six different filters. Most of the data come from the 1.23 meter Zeiss reflector of Calar Alto Observatory, used in the official time of the Andalusian Network for Technological and Scientific Public Outreach (RECTA), together with the Documentary School of Astrophotograpy (DSA). The images were obtained with different integration times through narrow-band filters centered on the emission lines H-alpha and O-III, until completing 18 hours of exposure time as a whole. These data were complemented with wide-band images (filters Johnson B, V and R) obtained with the 3.5 meter Zeiss telescope of Calar Alto, equipped with the camera LAICA, with a total integration time of 3 hours, under poor weather conditions. Also, the image contains 45 minutes of archival infra-red observations performed with the same telescope and the infrared camera Omega 2000, centered on the emission line of molecular hydrogen (2.12 micrometers), that helps to better define the wavefronts in the external, faint halo of the nebula. The narrow-band images were combined with the wide-band ones coding them as three different color hues: cyan for O-III, red for H-alpha (that, combined with H-beta, gives a violet color as a result), and red for molecular hydrogen. The data were processed by Vicent Peris, Jack Harvey, Steve Mazlin and José Luis Lamadrid with the program PixInsight. The image covers 10 by 11 arcminutes on the sky. Celestial north is up, celestial east is left.
The extraordinary quality of this image is due to several factors: the quality of the sky during the observations with the 1.23 m telescope, the instruments used, a detailed planning of the observations, and an extremely careful data process. The deconvolution process, applied over the areas with higher signal level, was combined with noise reduction to yield one of the most detailed visions of M57 ever got from the Earth surface. The technique of wavelet decomposition preserves the details of structures with different sizes, and over the whole range of brightness. This way, colors and subtle details are not lost, the stars do not get saturated and stellar colors are evident in all cases except in the extremely bright stars. Check, for instance, the chromatic contrast between the two bright stars inside the nebular hole: the white-bluish hue of the central white dwarf is clearly distinguished from the reddish aspect of the second star, that appears in the line of sight just by chance and bears no relation to the nebula.
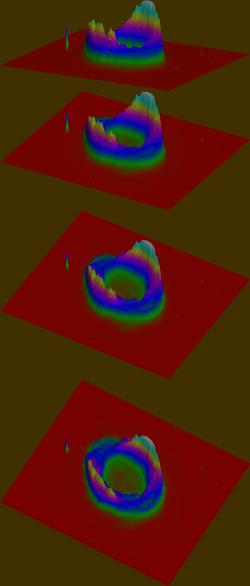
This three-dimensional plot of the linear H-α image has been produced with the 3DPlot JavaScript script in PixInsight. It shows that even the hole at the center of the nebula's main disk has a very steep illumination fall with respect to the ring. Deconvolving the outer halo of M57 —barely visible in the graphs due to its faintness— would be impossible due to the extreme weakness of the signal on these areas of the image. Click on the figure to see a larger image.
The different spectral contributions to the image are shown in separate panels on this sequence. From left to right: emission from ionized oxygen (OIII), from ionized hydrogen (H-α), from molecular hydrogen (H2, infrared light), and the final three color channels blue, green and red. The letters overimposed on each panel indicate the color hue with which each contribution has been entered into the final RGB image. Click on the figure to download a larger image.
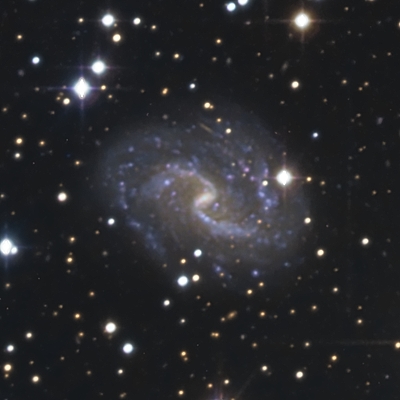

The image captures IC 1296 the nebula (central zone and halo), but also a large amount of stars of all colors and an overwhelming quantity of background galaxies. The morphology and color of many of them can be easily seen. Especially outstanding is the barred spiral galaxy IC 1296 (image to the right), placed at 300 million light-years. A walk across the image reproduced at full size reveals many other galaxies set up as background for field stars (all of them belonging, of course, to our own Galaxy).
All the material on this page is copyright. Feel free to use it for personal study or evaluation purposes exclusively. Any other use, including without limitation the public reproduction, online storage and generation of derivative works, is strictly prohibited without prior written consent from Pleiades Astrophoto S.L.