PixInsight 1.6.1 introduces four new console-based commands:
lsimg,
lsws,
lskwd and
hash. This is a brief list with manual pages. Note that the same information is available with the standard help command (e.g. 'help lsimg'), or by running the commands with the standard --help argument (e.g. 'lsimg --help').
lsimg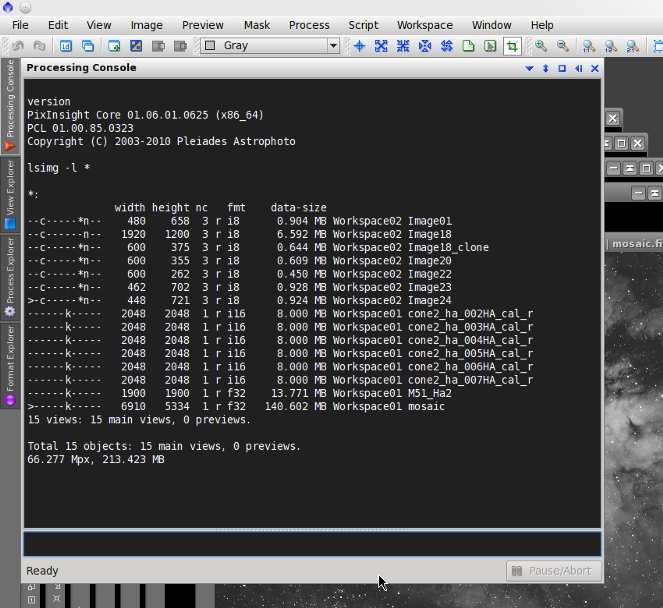
The lsimg command writes information about views and their contained images.
Usage: lsimg [<arg_list>] [<image_id_list>]
-W[=<ws_id>|<ws_idx>] | -workspace[=<ws_id>|<ws_idx>]
Restricts view listing to a given workspace. When the optional <ws_id>
is specified, only views pertaining to a workspace whose identifier is
<ws_id> will be listed. When the optional <ws_idx> is specified, output
is restricted to the workspace whose index is <ws_idx> >= 0. When no
workspace identifier or index is specified, lsimg restricts view listing
to the current workspace.
-s | -short
Enables the short listing mode. In short listing mode, only the view
identifiers are written. (default=short)
-l | -long
Enables the long listing mode. In long mode, lsimg prints flags and
numerical data for each view. The following information is written
in tabular format:
f1f2f3f4f5f6f7f8f9fafbfc w h n R f s u W v
f1 : > if the view is the current view, - otherwise.
f2 : p if the view is a preview, - otherwise.
f3 : c if the view is a color image, - if it is a grayscale image.
f4 : l if the view uses a local RGBWS, - if it uses the global RGBWS.
f5 : I if the image has an embedded ICC profile, - otherwise.
f6 : P if color proofing is enabled for this image, G if gamut check is
enabled, - otherwise.
f7 : k if the image has embedded FITS keywords, - otherwise.
f8 : m if the image has embedded XML metadata, - otherwise.
f9 : * if the view is modified, - otherwise.
fa : n if the image window contains a newly created image, u if the
image has been downloaded from a remote URI, - if the image has
been read from a local file.
fb : c if the image has been read as a copy of a local file, - otherwise.
fc : i if the image window is iconic, - otherwise.
w : width of the image in pixels.
h : height of the image in pixels.
n : number of channels in the image.
R : r if the image has real pixels, c if it is a complex image.
f : sample data format: i<n> or f<n>, where i indicates an integer
format and f a floating point format, and <n> is the sample size
in bits (8, 16, 32, 64 or 128).
s : size of the pixel data.
u : size units.
W : workspace identifier.
v : full view identifier.
-L | -very-long
Same as -l, but the full file path and URI (when applicable) are also
written for each view, on separate text lines.
--help
Displays this help and exits.
Without arguments, lsimg prints information for the current view.
lsws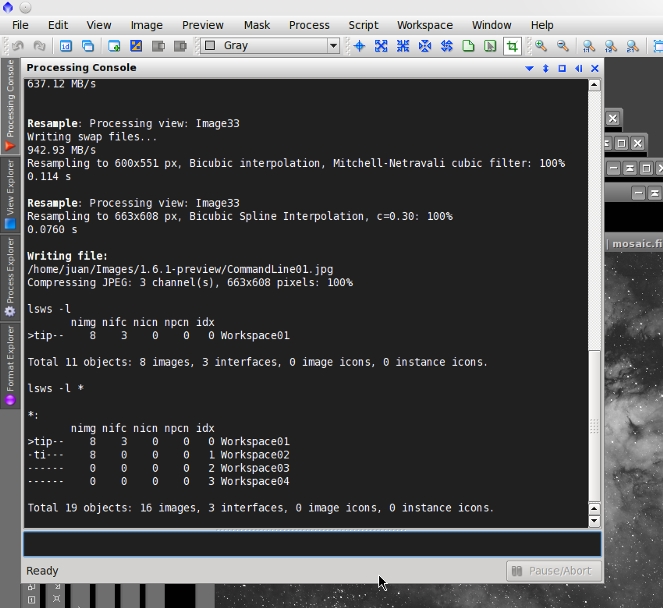
The lsws command writes information about workspaces and their contained objects.
Usage: lsws [<arg_list>] [<ws_id_list>]
<ws_id_list>
Defines a set of workspaces by their identifiers. The standard ? and *
wildcards are allowed and interpreted in the usual way.
-s | -short
Enables the short listing mode. In short listing mode, only the
workspace identifiers are written. (default=short)
-l | -long
Enables the long listing mode. In long mode, lsws prints flags and
numerical data for each workspace. The following information is
written in tabular format:
f1f2f3f4f5f6 ni np nm nn w W
f1 : > if the workspace is the current workspace, - otherwise.
f2 : t if the workspace has top-level child windows, - otherwise.
f3 : i if the workspace has visible images, - otherwise.
f4 : p if the workspace has visible process interfaces, - otherwise.
f5 : m if the workspace has image icons, - otherwise.
f6 : n if the workspace has instance icons, - otherwise.
ni : number of visible image windows in the workspace.
np : number of visible process interfaces in the workspace.
nm : number of image icons in the workspace.
nn : number of instance icons in the workspace.
w : workspace index.
W : workspace identifier.
--help
Displays this help and exits.
Without arguments, lsws prints information for the current workspace.
lskwd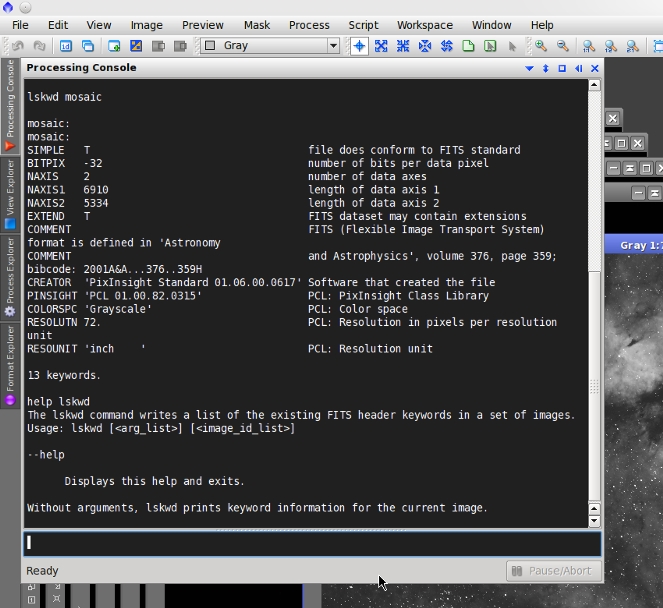
The lskwd command writes a list of the existing FITS header keywords in a set of images.
Usage: lskwd [<arg_list>] [<image_id_list>]
--help
Displays this help and exits.
Without arguments, lskwd prints keyword information for the current image.
hash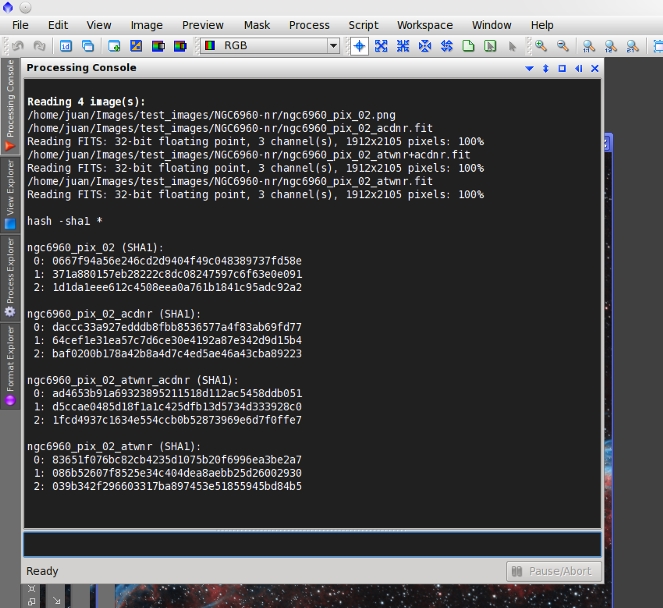
The hash command computes cryptographic hash digests of images.
Usage: hash [<arg_list>] [<image_id_list>]
-a=<alg> | -algorithm=<alg>
Specifies a cryptographic hash algorithm. <alg> can be one of the
following:
md4, md5, sha1, MD4, MD5, SHA1
Lowercase and uppercase variants have the same meaning. (default=md5)
-md4
-md5
-sha1
Specify a cryptographic hash algorithm. These arguments are equivalent
to their corresponding counterparts for the -a argument.
-c=<n> | -channel=<n>
<n> is a valid channel index (zero-based). By default, message digests
are computed for all channels of the target images(s). The specified
channel must exist on all subsequent target images, or a runtime error
will occur. (default=all).
--help
Displays this help and exits.